TESTICULAR REJUVENATION FOR MALE
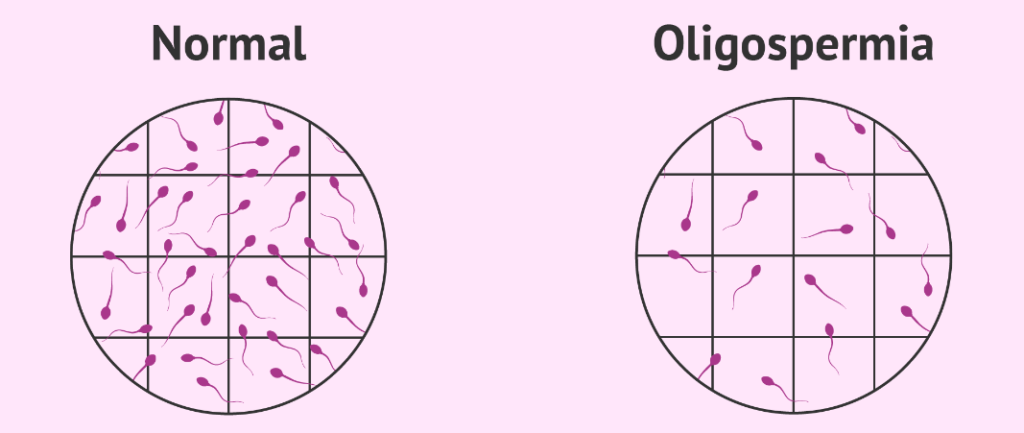
Oligospermia
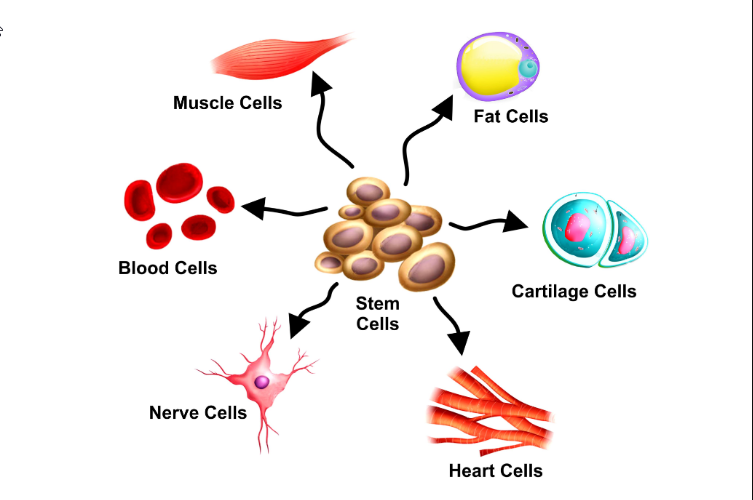
The therapeutic potential of stem cells has been tested in several in vitro, preclinical and clinical studies; and has confirmed their role in gamete production in conditions like oligospermia, characterized by limited production of sperms. Fortunately, technology has now enabled us to offer the stem cell secretome, possessing the same therapeutic and regenerative potential as that of parent stem cells.
Extracellular vesicles, also known as exosomes are the snapshot of secreting cells along with the same content as that of original cells; and are found to be highly effective in reversing various reproductive disorders due to their ability to promote cellular regeneration through enhanced cell signaling, better secretion of several essential growth factors and genetic manipulation through epigenetic changes.
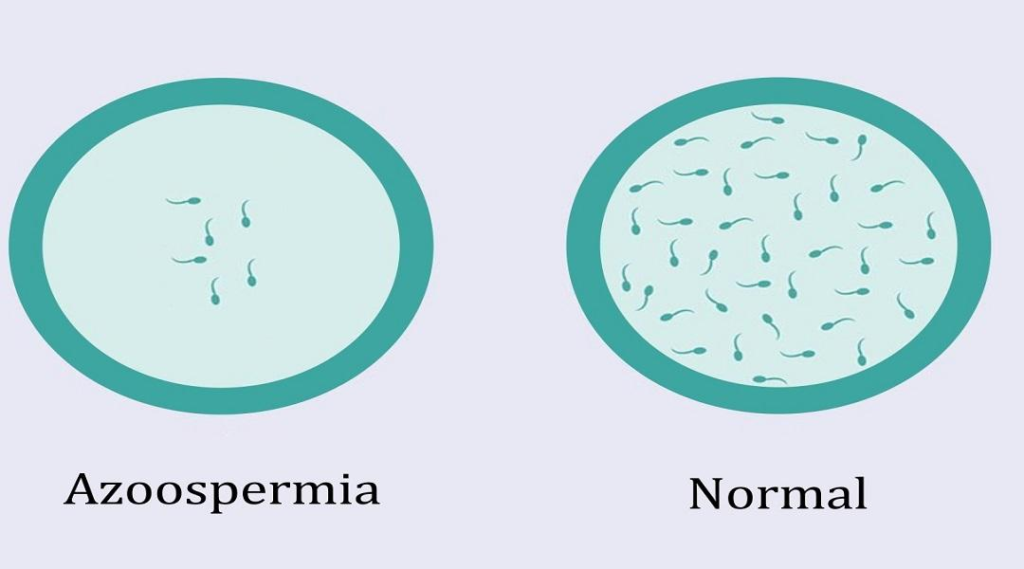
Azoospermia
Azoospermia is a condition characterized by zero sperm production and it accounts for 20-30% of the fertility-related issues in men. Advanced research on stem cells has suggested that the multi-differentiation potential of stem cells helps in hormonal regularization, regeneration of male germ cell epithelium, and production of sperms; increasing the chances of a reversal of fertility issues.
Besides, stem cells when administered along with exosomes can enhance cellular communication through increased activities and paracrine actions; which further takes care of genetic dysfunctions associated with no sperm production.
We have mastered and successfully applied this technique in clinical practice, helping a major chunk of patients to revive spermatogenesis and enjoy fatherhood.
Severe Oligoasthenospermia
Oligoasthenozoospermia or oligoasthenospermia (OA) is a sperm disorder that involves two disorders at the same time:
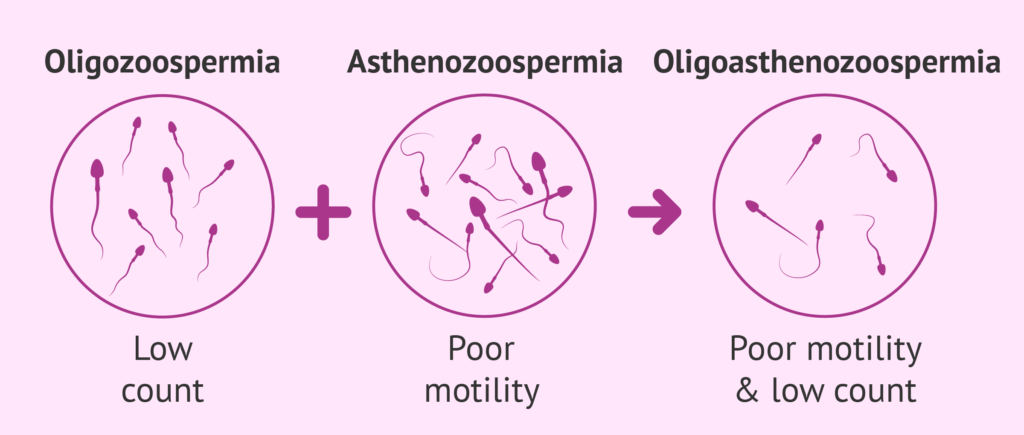
Oligozoospermia
Low sperm count, below 15 million sperm/ml.
Asthenozoospermia
Abnormal sperm motility, with more than 60% of sperm being immotile, or unable to move in a straight direction.
Teratozoospermia
Teratozoospermia is the abnormal sperm morphology, caused by defects in the head, midpiece, and/or tail. According to the criteria published in 2010 by the World Health Organization (WHO), a man has teratozoospermia when more than 96% of the sperm he produces are abnormally shaped.
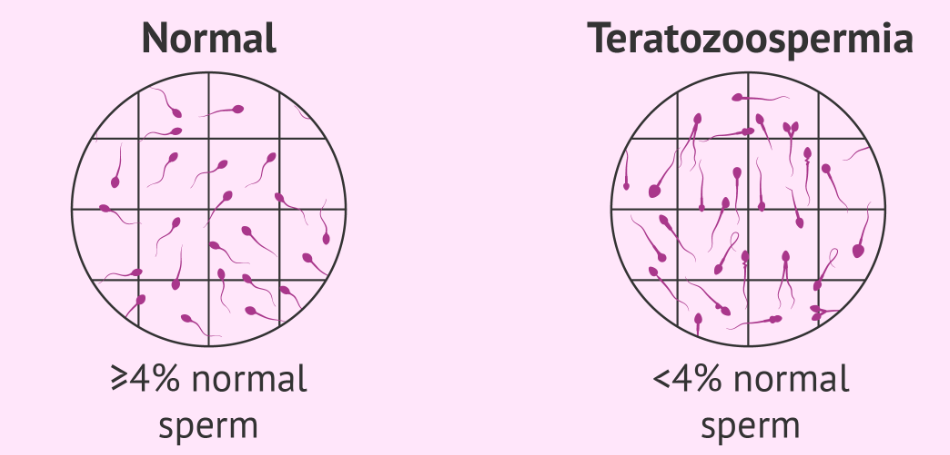
Teratozoospermia is associated with male infertility in all cases, as it means that sperm are unable to get to the egg due to their abnormal shape.
The causes of abnormal sperm morphology are varied and, in most cases, difficult to determine.
The following are the most common ones:
- Genetic traits
- Cancer treatments (chemotherapy and radiotherapy)
- Bacterial infections in sperm and orchitis
- Testicular trauma
- Testicular disorders, like varicocele
- Fever
- Diabetes mellitus (DM) or meningitis
- Tobacco, alcohol, and street drug use
- Unhealthy habits: unbalanced diet, exposure to toxic substances, too tight clothes, etc.
OVARIAN REJUVENATION FOR FEMALE
Ovarian Failure
Premature ovarian failure (POF), or premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), is a condition that occurs when a person’s ovaries stop producing eggs regularly before they reach the age of 40.
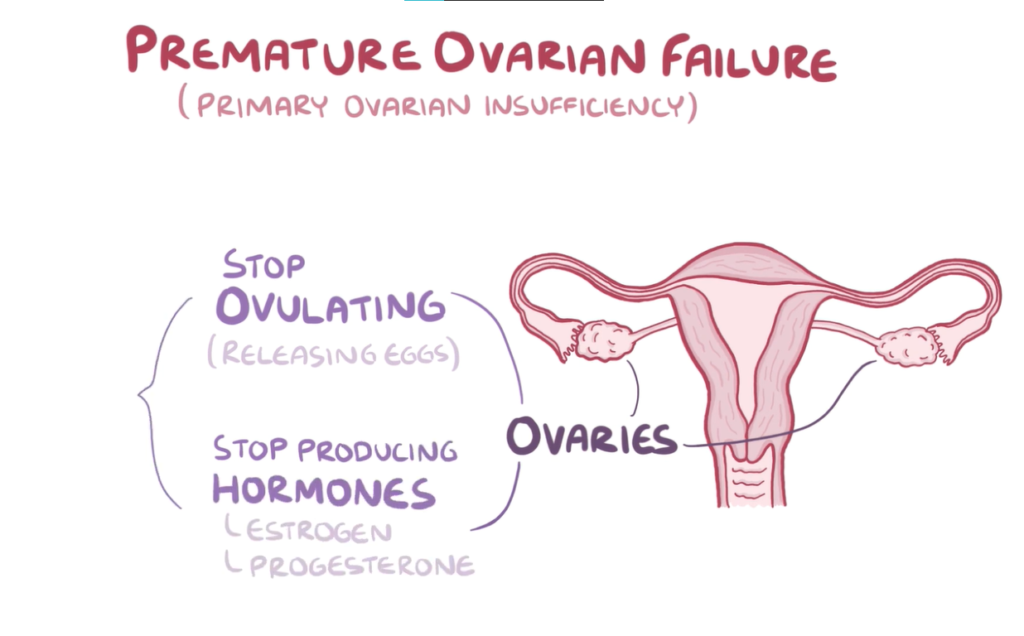
This can make it difficult for someone to become pregnant.
Common symptoms of POI include:
- Night sweats
- Hot flashes
- Trouble becoming pregnant
- Painful sex due to thinning of the vaginal lining
- A decrease in sex drive
- Irregular periods
- No periods (amenorrhea)
- Irritability
- Vaginal dryness
- Few or no signs of puberty as a teenager
Poor Ovarian Reserves
Ovarian reserve refers to the number and quality of your eggs, also known as oocytes. If you have diminished ovarian reserve, this means that the number and quality of your eggs are lower than expected for your age. Diminished ovarian reserve can affect people of all ages.
Aging naturally reduces your egg reserves. However, several other factors can cause diminished ovarian reserve. These include:
- Tubal disease
- Endometriosis
- Prior ovarian surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Smoking
- Pelvic infection
- Autoimmune disorders
- Mumps
- Genetic abnormalities such as fragile X syndrome